Building Design: The Importance of Azimuth Angle
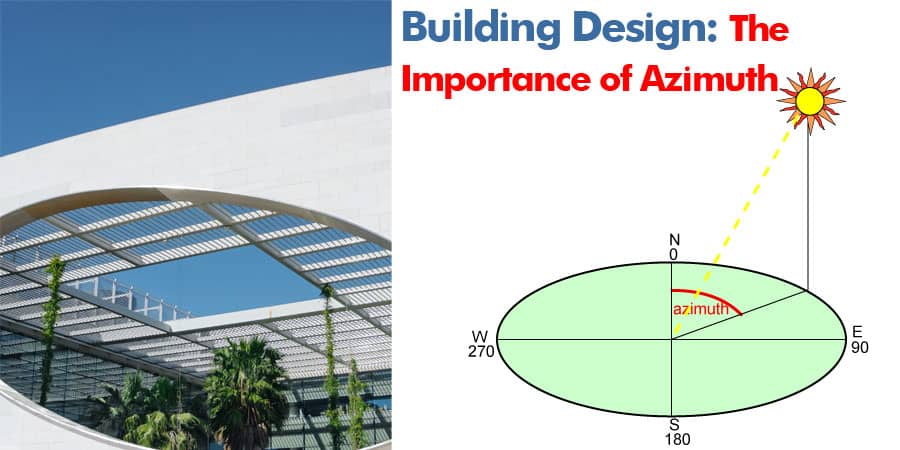
Azimuth Angle
When it comes to building design, there are many important factors to consider. One factor that is often overlooked, but can have a significant impact on the building's performance, is the azimuth angle.
The azimuth angle is the angle between true south and the direction in which a building faces. This angle plays a critical role in determining how much sunlight a building receives throughout the day and throughout the year. Buildings that are properly oriented to take advantage of the sun's path can benefit from increased natural lighting and reduced energy costs for heating and cooling.
In addition to its impact on lighting and energy usage, the azimuth angle can also affect the overall comfort of the building's occupants. Buildings that are oriented to face prevailing winds can benefit from increased natural ventilation, which can help to reduce the need for mechanical ventilation systems and improve indoor air quality.
The importance of the azimuth angle is particularly evident in the design of passive solar buildings, which are designed to take advantage of the sun's path to provide natural heating and cooling. These buildings typically have large south-facing windows to maximize solar gain during the winter months, and overhangs or shading devices to minimize solar gain during the summer months.
Overall, the azimuth angle is an important consideration in building design, as it can have a significant impact on energy usage, indoor comfort, and overall building performance. Architects and designers should carefully consider the orientation of a building during the design process, in order to optimize its performance and minimize its environmental impact.
Passive Solar Design
In addition to passive solar design, the azimuth angle can also be important for buildings with active solar systems, such as photovoltaic (PV) panels or solar thermal collectors. PV panels are most efficient when they are facing directly towards the sun, which means that the azimuth angle should be taken into account when determining the optimal location for the panels. Solar thermal collectors, on the other hand, are typically mounted on a tracking system that follows the sun's path throughout the day, so the azimuth angle is less critical for these systems.
The azimuth angle can also be important for buildings that rely on daylighting, or the use of natural light to illuminate interior spaces. Daylighting can help to reduce energy usage and improve the visual comfort of occupants, but it requires careful consideration of the building's orientation and window design. Buildings that are properly oriented can benefit from a consistent level of natural light throughout the day, while buildings that are poorly oriented may experience glare or uneven lighting.
Overall, the azimuth angle is just one of many important factors to consider in building design. Other factors, such as building orientation, window placement, and shading devices, can also have a significant impact on building performance. Architects and designers must balance these factors in order to create buildings that are efficient, comfortable, and aesthetically pleasing.
To determine the optimal azimuth angle for a building, designers can use a variety of tools and techniques, such as computer simulations, sun path diagrams, and site analysis. Computer simulations allow designers to model the building's performance under different conditions and adjust the design accordingly. Sun path diagrams provide a visual representation of the sun's path throughout the year, which can be used to determine the best orientation for the building. Site analysis involves observing the site's natural features, such as topography and vegetation, and taking them into account when designing the building.
In addition to these tools, designers can also consult building codes and standards to ensure that their designs meet minimum requirements for energy efficiency and sustainability. For example, the International Energy Conservation Code (IECC) sets minimum requirements for building orientation and window placement, while LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) certification requires buildings to meet certain performance criteria related to energy usage, water efficiency, and indoor environmental quality.
Summary
In summary, the azimuth angle is an important consideration in building design, as it can have a significant impact on energy usage, indoor comfort, and overall building performance. Designers must carefully consider the orientation of the building, as well as other factors such as window placement and shading devices, in order to create buildings that are efficient, comfortable, and sustainable. By incorporating these factors into their designs, architects and designers can help to create a more sustainable built environment for future generations.
