Reinforced Concrete Design Of Tall Buildings
Introduction
Tall buildings are architectural marvels that shape modern city skylines. The design and construction of tall buildings require careful consideration of structural systems and materials to ensure safety, stability, and durability. Reinforced concrete has emerged as a popular choice for tall buildings due to its numerous advantages.
Importance of Reinforced Concrete in Tall Buildings
Strength and Durability
Reinforced concrete offers excellent strength and durability, making it well-suited for tall buildings. The combination of concrete's compressive strength and steel reinforcement's tensile strength allows reinforced concrete structures to withstand the vertical and lateral loads experienced by tall buildings.
Fire Resistance
Fire safety is a critical consideration in tall buildings. Reinforced concrete has inherent fire-resistant properties, as it does not burn or release toxic gases under high temperatures. This makes it a preferred choice for structural elements that require enhanced fire protection.
Flexibility in Design
Reinforced concrete provides flexibility in design, allowing architects and engineers to create unique and aesthetically pleasing tall buildings. The ability to mold and shape concrete into various forms enables the construction of complex geometries and innovative architectural features.
Structural Considerations for Tall Buildings
Vertical Loads
Tall buildings must be designed to withstand various vertical loads. These loads include:
Dead Loads
Dead loads refer to the weight of permanent structural elements, finishes, and equipment. The design must account for the self-weight of reinforced concrete elements, such as columns, beams, slabs, and walls.
Live Loads
Live loads are transient loads caused by the occupancy and use of the building. These include the weight of people, furniture, equipment, and other movable loads. Tall buildings must be designed to accommodate live loads based on their intended use and occupancy.
Lateral Loads
Lateral loads are horizontal forces acting on a building, which are particularly significant in tall structures. The two main types of lateral loads are:
Wind Loads
Tall buildings are exposed to considerable wind forces due to their height and exposure. The design must account for wind loads to ensure the building can withstand these forces without excessive deflection or structural failure. Wind tunnel testing and computational analysis are often employed to determine the wind loads on different parts of the building.
Seismic Loads
In earthquake-prone regions, tall buildings need to be designed to withstand seismic forces. Reinforced concrete structures can effectively dissipate seismic energy and resist the lateral forces caused by earthquakes. Proper analysis and design techniques, such as the incorporation of seismic-resistant features like shear walls and damping systems, are crucial in ensuring the safety of tall buildings.
Design Considerations for Tall Buildings
Designing tall buildings requires careful consideration of various factors, including:
Foundation Design
The foundation of a tall building is critical for transmitting loads to the ground and ensuring stability. The design must consider the soil conditions, load distribution, and settlement control to prevent foundation failure.
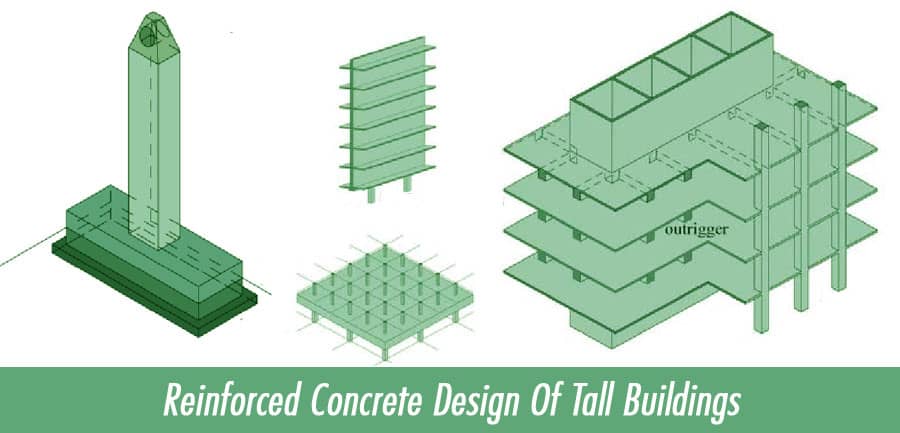
Column and Beam Design
Columns and beams provide vertical and horizontal support to the building. Their design involves selecting appropriate dimensions, reinforcement detailing, and considering load-bearing capacity to ensure structural integrity.
Floor System Design
The floor system in tall buildings should be designed to withstand vertical loads, distribute them to the supporting columns, and accommodate the required functionality. Slabs, beams, and shear walls play vital roles in providing strength and stability to the overall structure.
Reinforcement Detailing
Reinforcement detailing involves determining the size, spacing, and arrangement of reinforcement bars in structural elements. Proper reinforcement detailing ensures the integrity and load-carrying capacity of the reinforced concrete members.
Advancements in Reinforced Concrete Design for Tall Buildings
Continuous advancements in reinforced concrete design have further improved the construction of tall buildings. Some notable advancements include:
High-Strength Concrete
High-strength concrete allows for the use of thinner sections and reduced structural elements, enabling more efficient designs and increased usable space in tall buildings.
Fiber Reinforced Concrete
The addition of fibers, such as steel or synthetic fibers, to concrete enhances its crack resistance and ductility. Fiber reinforced concrete can provide improved performance in terms of durability, impact resistance, and resistance to shrinkage and cracking.
Post-Tensioning
Post-tensioning is a technique used to strengthen and optimize concrete members by introducing prestressing forces. This method improves the load-carrying capacity and performance of tall building elements, such as beams and slabs.
Conclusion
Reinforced concrete has become a preferred choice for the design and construction of tall buildings due to its strength, durability, fire resistance, and design flexibility. By considering the vertical and lateral loads, along with appropriate design considerations, engineers and architects can create safe and efficient tall buildings that stand the test of time. The continual advancements in reinforced concrete design techniques further enhance the possibilities and performance of tall buildings.
FAQs
Can other materials be used in combination with reinforced concrete in tall buildings?
Yes, other materials such as steel, glass, and composite materials can be used in combination with reinforced concrete to achieve specific design goals and architectural aesthetics in tall buildings.
Are there any height restrictions when using reinforced concrete in tall buildings?
There are no specific height restrictions for using reinforced concrete in tall buildings. The design considerations and structural analysis become more complex as the height increases, requiring careful engineering and expertise.
Can reinforced concrete be used in seismic-prone areas for tall building construction?
Yes, reinforced concrete can be effectively used in seismic-prone areas for tall building construction. Proper design techniques, such as incorporating seismic-resistant features and adhering to seismic codes, are essential to ensure the safety and performance of the structure during earthquakes.
What are the advantages of using post-tensioning in tall building design?
Post-tensioning allows for longer spans, reduced beam depths, and increased floor-to-ceiling heights in tall buildings. It provides structural efficiency, minimizes the use of materials, and enhances the overall performance and load-carrying capacity of concrete members.
