Construction slabs: types, uses, and applications
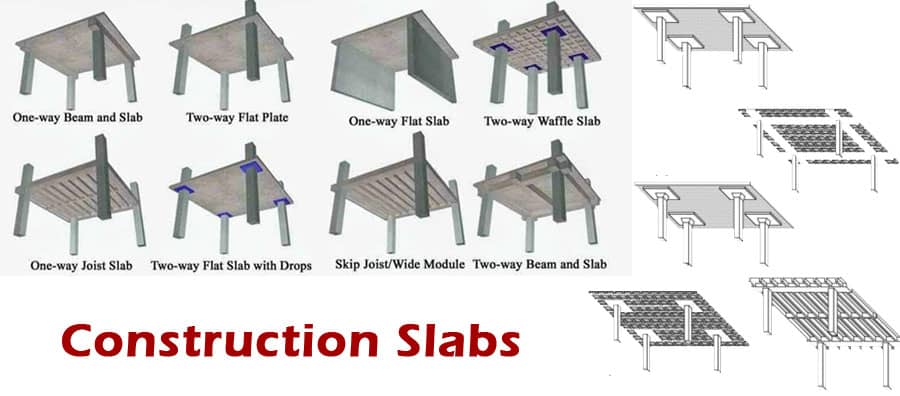
Definition of Slabs
A slab can be defined as a flat, horizontal structural element made of reinforced concrete that acts as a load distribution point; for example, the slab receives a load from the beams through the columns to the footings and ultimately to the soil below. Structures that bear loads are supported by slabs and structures which bear loads are supported by frames.
Slab construction differs from one method to another depending on the type of slab to be constructed. Slabs can be used for floors or roofs, depending on what they are used for. In contrast to the live load acting on the roof slabs, the living load acting on the floor slabs is considerably greater.
Various types of Slabs
The following are some of the types of slabs that are available, along with their benefits and drawbacks, which are mentioned below:-
Conventional Slab type
A typical slab is one that is supported by beams and columns. Slabs with traditional thickness are modest, but beams with substantial depth are common. From the slab to the beam, the load is transferred before going from the beam to the column.
These slabs are reinforced by horizontal and vertical bars, with the vertical bar referred to as the distribution bar and the horizontal bar as the major reinforcement.
Benefits
- It is easy to conduct these slabs since they are made from concrete.
- There is no need for skilled labor to install these slabs.
- Electricity, mechanical, and plumbing installations can be completed quickly and easily.
- There is nothing complicated about the formwork of these Slabs.
Drawbacks
- There is nothing structurally significant about the concrete used in the tension zone but it is provided to simplify the construction process.
- These slabs cannot be removed from their formwork during curing.
Flat Plate type
As opposed to conventional slabs, flat plates do not transfer loads from one slab to a beam, they instead transfer loads from one slab to another. A flat plate is a type of plate that directly transfers the load from the columns to the plate. There are two ways of implementing the flat plate system, depending on the design plan that has been developed.
Benefits
- There is no beam involved in the formwork, which simplifies the slabs.
- The absence of the beams allows for a reduction in the height of the floor, which results in a lower floor height.
- A mechanical installation and an electrical installation can be easily installed without the need for bending.
Drawbacks
- Since there are no beams to support the structure, special consideration must be given to the shear forces because there are none.
- In general, flat plates are not suitable for partitions made of brittle materials such as brick masonry.
Waffle Slab type
On their soffit, waffle slabs have hollow grid systems that are similar to those of hollow grids. These slabs are lightweight. In addition to reducing the weight of the slab, the hollow grid system improves its structural stability by reducing its self-weight. As a result of this reinforcement, the space between the ribs is occasionally treated as a beam and treated as a supporting structure to increase the slab's flexural rigidity.
Benefits
- Due to the lighter sections of these slabs, they possess a lower self-weight, thus leading to the foundations being more economically sound.
- This type of Slab formwork is very economical when it is coordinated in a modular way.
- Compared to conventional slabs, these slabs have a much higher load carrying capacity.
Drawbacks
- It is a tedious process to construct waffle slabs because a special formwork is needed for them, which is extremely complex.
- It is not economical to increase the height between the floors due to the increased height of these slabs.
Hollow deck Slab type
Hollow deck slabs are one of the most popular types of prefabricated concrete slabs available in the market that use the principles of how stress develops in a section in order to design the slab. There is compression and tension in the structure, which is provided by the concrete as well as the steel. Besides providing a solid section, the concrete in the tension zone serves no specific purpose.
Benefits
- Because of lighter sections and therefore less self-weight, slabs with lighter sections lead to more economical foundations
- Using this slab, you can construct long spans.
- The fuller, more pleasing appearance of this slab can be appreciated from below.
Drawbacks
- To install this slab skilled professionals are required.
- These slabs are much more complicated to get replaced or repaired.
Hardy Slab type
It is a special type of slab consisting of a uniform pattern of hardy bricks embedded within them, which makes them a special type of slab. There are hollow concrete blocks that are used in making hardy bricks. In regions where the temperature is high, this type of slab is mainly used. Consequently, a deeper slab is required, which leads to a greater slab thickness.
Benefits
- In addition to their lighter sections, these slabs are more economical because they have less self-weight.
- It improves the sound and heat insulation of the slabs by providing hollow spaces.
Drawbacks
- In order for hardy slabs to be constructed, sophisticated formwork needs to be used and this can be time-consuming.
- For small projects, this is not an economical option.
