Ready Mix Concrete Quality Control Plan and Its Testing
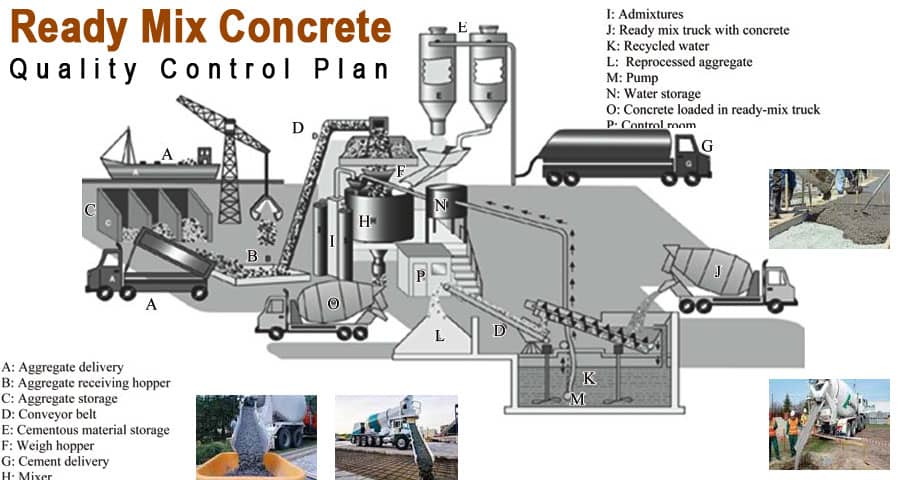
In modern construction, Ready Mix Concrete (RMC) has become a cornerstone of quality, consistency, and speed. However, achieving top-tier concrete performance hinges entirely on a robust Quality Control (QC) Plan. The integrity of any concrete structure - bridges, highways, commercial buildings, or residential complexes - relies on how precisely the RMC is tested, controlled, and monitored. Our comprehensive RMC Quality Control Plan ensures every batch meets stringent performance, durability, and compliance standards.
Objectives of a Ready Mix Concrete Quality Control Plan
The primary goals of an RMC QC plan are:
- Consistency in concrete strength and durability
- Reduction in material waste and rejection
- Compliance with IS codes and customer specifications
- Minimization of errors in mix design and batching
- Ensuring sustainability through efficient raw material usage
Key Components of a Ready Mix Concrete Quality Control Plan
1. Raw Material Selection and Testing
The foundation of a high-quality mix starts with rigorous material quality verification:
- Cement: Regular testing for fineness, setting time, soundness, and compressive strength.
- Fine Aggregate (Sand): Checked for silt content, gradation, and moisture content.
- Coarse Aggregate: Assessed for shape, size distribution, crushing value, and abrasion resistance.
- Water: Tested for pH, alkalinity, chlorides, and sulphates as per IS 456:2000.
- Admixtures: Evaluated for compatibility, dosage, and setting properties.
Each material undergoes routine inspection and is stored separately to avoid contamination.
2. Concrete Mix Design Process
Our mix designs are developed according to IS 10262 and verified through trial mixes:
- Target Mean Strength Calculation
- Selection of Water-Cement Ratio
- Determination of Cement Content
- Admixture Optimization
We prepare multiple trial batches to validate workability, slump, air content, and strength development across 7, 14, and 28 days. Every design is backed by laboratory results and field validations.
3. Batching and Mixing Controls
Our RMC plants are equipped with fully automated batching systems that guarantee precision:
- Automated Weight Batching: Ensures ±1% accuracy in cement and ±2% in aggregates.
- Moisture Sensors: Adjust water content dynamically based on real-time aggregate moisture.
- Mixing Time Monitoring: Each batch is mixed for a controlled duration to avoid over or under-mixing.
Batching data is logged for every load and routinely cross-verified with manual checks to prevent deviations.
4. Transportation and Delivery Protocols
Concrete is delivered in transit mixers within a strict timeframe (preferably <90 minutes). To uphold freshness and workability:
- Dispatch Tickets: Include batch details, slump, and time of dispatch.
- GPS Tracking: Monitors delivery route and estimated time.
- On-Site Slump Adjustment: Water or admixtures added only by QC personnel with proper documentation.
5. On-Site Quality Checks and Testing
The site QC engineer verifies incoming concrete against project specifications using:
- Slump Test (IS 1199): Conducted for each truckload to check workability.
- Temperature Checks: Ensures concrete is within 30°C for hot regions.
- Casting of Test Cubes: Usually 3 or 6 cubes per 100 m3, tested at 7 and 28 days for compressive strength as per IS 516.
- Air Content Measurement: For air-entrained concrete, tested using pressure methods.
Rejected concrete is immediately documented and either recycled or disposed of per environmental regulations.
Routine Laboratory Tests for Quality Assurance
To maintain RMC plant certification and ISO compliance, we conduct the following tests regularly:
Fresh Concrete Testing
- Slump (Workability)
- Unit Weight
- Air Content
- Temperature
Hardened Concrete Testing
- Compressive Strength (IS 516)
- Flexural Strength (IS 516 Part 2)
- Modulus of Elasticity
- Water Permeability
- Rapid Chloride Penetration Test (RCPT)
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT)
- Rebound Hammer Test (IS 13311 Part 2)
- Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity (IS 13311 Part 1)
These are often used for auditing hardened concrete and assessing in-situ strength.
Documentation and Traceability
All testing and QC activities are thoroughly documented:
- Material Test Certificates
- Calibration Records
- Mix Design Approvals
- Daily QC Logs
- Concrete Pour Cards
Each concrete load is traceable from the raw material batch to its final placement point at the construction site.
Personnel Training and Certification
Our technicians and engineers are trained under National Ready Mixed Concrete Association (NRMCA) and Quality Council of India (QCI) programs. Regular training sessions ensure:
- Updated knowledge on IS codes
- Improved sampling and testing methods
- Efficient troubleshooting at site
We believe a well-trained QC team is the backbone of a successful RMC operation.
Corrective and Preventive Actions
Any non-conformance identified during testing leads to immediate Root Cause Analysis (RCA). Depending on the issue, actions include:
- Adjusting mix proportions
- Replacing defective material
- Retraining staff
- Auditing batching processes
A log of all such actions ensures continuous improvement and learning.
Environmental and Safety Compliance
Our QC plan integrates eco-friendly practices:
- Use of fly ash or GGBFS as cement replacement
- Effluent treatment and recycling of wash water
- Dust suppression measures at plant
- PPE usage and safety briefings during sampling and testing
We strive to produce concrete that is not just strong but sustainable and safe.
Conclusion
A rigorous Ready Mix Concrete Quality Control Plan is essential to deliver concrete that performs well structurally and endures environmental conditions for decades. With disciplined adherence to testing standards, documentation, mix optimization, and personnel training, we ensure reliability, compliance, and customer satisfaction.
Please watch the following short video for Ready Mix Concrete Quality Control Plan and Its Testing
