Caisson Foundation and How is it Used
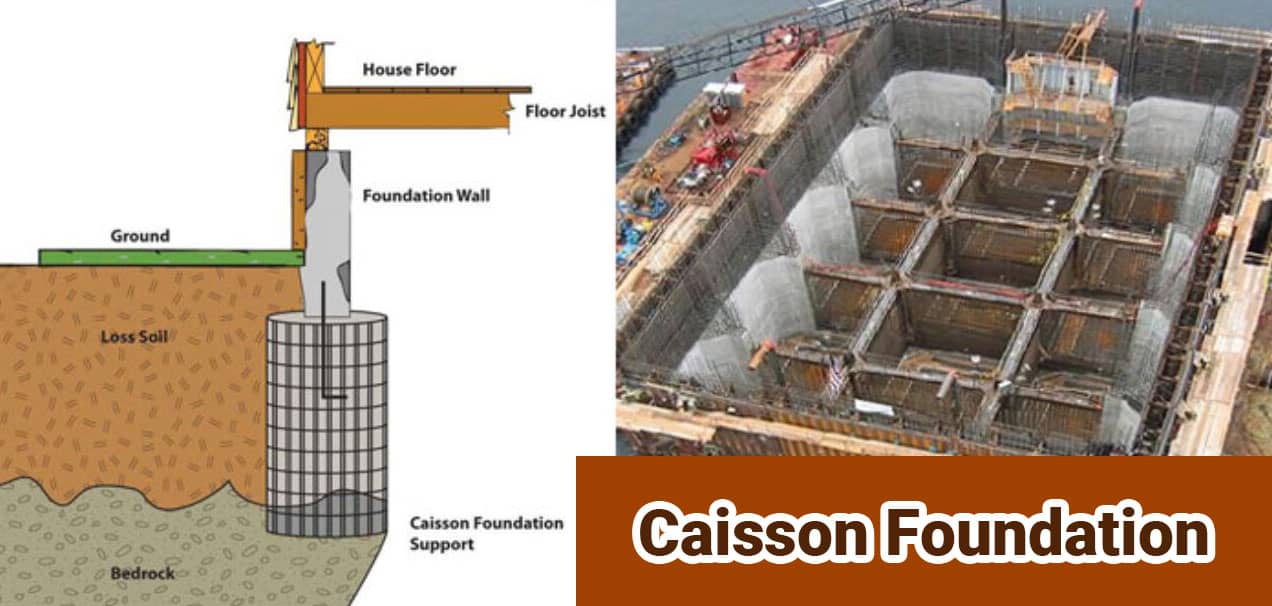
A Caisson Foundation is principally a penetrable box with the top open. It's sunk into water to gain access to the bed of the sluice. It's generally made of wood, sword or concrete depending upon design demand.
Through this cuboid chamber, the workmen can make construction work at the bottom of water bodies without being hampered by the water. Consequently, this is substantially used to place foundations at swash beds.
Caissons are generally made on reinforcement first. Also, They're launched into the water body. The locker is also floated to the designated spot. Also they're sunk vertically to the bottom. After icing that the locker is leakproof, the water inside is pumped out to dry.
Types of Caisson Foundation
Box Caisson
This is the most basic type of caisson. It is made of timber, concrete or steel. It is built on shore and floated to the foundation location and sunk to the bottom. It is basically a box without the top.
Open Caisson
This type of caisson has neither the top nor the bottom. When made in a cylindrical shape, it looks like a well without top or bottom. It can be built in many shapes - vertical, over, or any other option.
In case of building large bridges, a bathtub-like shape is preferred. Usually open caissons are made of steel plates welded together. RCC can be also used here, as the situation requires.
Pneumatic Caisson
This odd type of caisson has an open bottom but closed top. This has to be forced down to the bottom of the water by means of compressed air. Thus the name is derived. A pneumatic caisson consists of a working chamber, a shaft, and an airlock. The caisson is made of inner and outer layer of steel skins. Trusses and girders join them to form a boxlike structure.
The working chamber in curvaceous caissons is 3-4 measures altitudinous only. It's made watertight with a special seal on top. The locker's nethermost edge has a sword edge that cuts into the foundation. All this facilitates working within the chamber while the locker is being sunk. People can pierce the caison via the airlock.
One factor that needs to be especially watched for in curvaceous caissons is the air pressure within the working chamber. A normal human being can repel an air pressure of1.32 kilos per forecourt centimeter for eight hours in moderate comfort.
For lesser pressure, the work time inside a locker has to be reduced. Indeed also, the maximum air pressure allowed inside curvaceous caissons is3.75 kg/sq.cm. Also, you need to take care of contraction and relaxation sickness.
Advantages
- It is very economic.
- It minimizes pile cap needs.
- Working inside a caisson creates less vibration and noise.
- Caisson technology is highly flexible and can adapt to most construction needs on site.
- The caisson foundations have high axial and lateral loading capacity.
Disadvantages
- It is very sensitive to construction procedures.
- They are not good for using in contaminated sites.
- It needs qualified inspectors and constructing crew.
