Principal of Structural Construction
Classification of Buildings
Buildings and other structures are grouped based on the risk related with unacceptable performance of the structure, according to Table 1.1. The risk groups range from I to IV, where first I represents buildings and other structures that has no danger to human life in the event of failure and group IV represents all important facilities. Each structure is allocates the highest applicable risk group. Assignment of more than one risk category to the same structure based on and loading conditions is permitted.

Combination of Loads
Numerous types of loads that act on a structure are reported in the "Standard Unit Loads" section. For plotting a structure, its components, or its foundation, loads are reviewed to act in the following - amalgamation with load factors as indicated in order to produce the most unfavourable effect on the structure or its elements. Dead load, roof live load, floor live load, and snow load are gravity loads that act on the end of downward. Wind load and seismic load have upright as well as lateral elements. The on the end of acting roof live load, live load, wind load (simplified approach), and snow load are reviewed to be acting on the horizontal projection of any inclined surface. Nevertheless, dead load and the vertical elements of earthquake load act over the entire inclined length of the member.
Working Stress design and Structural Design
There are two perspective to design:
- the traditional approach and
- a comparatively newer approach
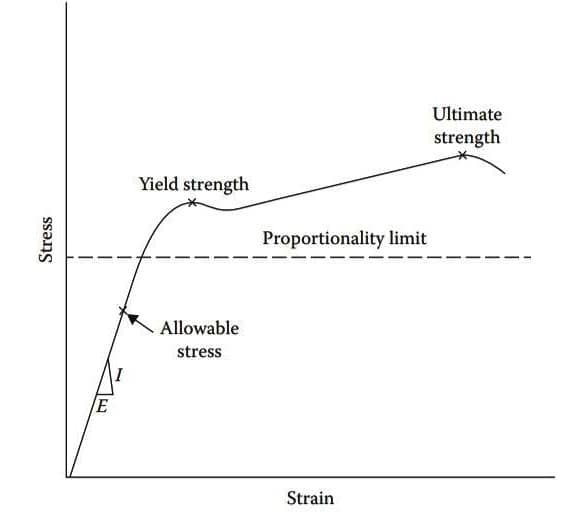
The difference between them can be understood from the stress - strain diagram. The diagram with labels for a manageable material is shown in the below diagram. The diagram for a brittle material is similar except that there is only one hump suggestions both the yield and the ultimate strength point and the graph at the starting is not really (but close to) a straight line.
Allowable stress is ultimate strength split by a factor of safety. It sinks on the straight-line section within the elastic range. In the allowable stress design (ASD) or working stress design method, the design is carried out so that when the calculated design load, known as the service load, is applied on a structure, the actual stress created does not exceed the allowable stress limit. Since the allowable stress is well within the ultimate strength, the building is secured. This technique is also known as the elastic design approach.

