Testing for silt content in Sand
Fine aggregate or Sand is one among the foremost important construction materials on any construction site. It should be selected very carefully because it contributes to the strength of varied important mixtures like concrete, ointments, and mortars.
Sand need to be tested for the presence of soil, silt, moisture, and other harmful materials (salts, coal, mica) which will affect the strength of a structure and cause avoidable reorientation.
Fine quality construction and features a particle size starting from about 150 mm to 4.75 mm. This causes smaller particles to be classified as silt.
The presence of high salt content (> 8%) within the SandSand reduces the bonding capacity of the staple and affects the strength and sturdiness of the work. Silt content testing is suggested for each 20 m3 of SandSand.
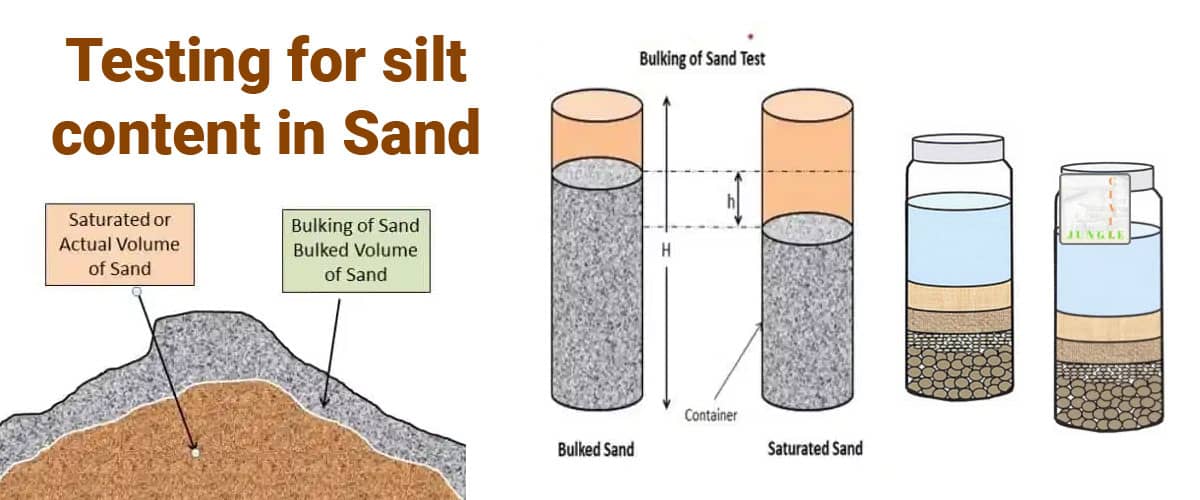
The sand caused to a vacant lot or other works may contain an amount of moisture, which can cause it, when loosely filled to a container, to occupy an outsized volume than it might occupy if dry.
If the sand is measured by loose volume, it's necessary in such a case to extend the measured volume of the sand, in order that the quantity of sand put to the concrete could be the quantity intended for the nominal mix used (based on dry sand).
It'll be necessary to extend the quantity of sand from the 'percentage' bulking. The correction to be made is merely a rough approximation since the system of measurement by loose volume may be a rough method at the best .
However, the correction of the proper order can easily be determined and must be applied so as to stay the concrete uniform.
