A Guide to Building Earthquake-Resistant Structures

As we are well aware, one cannot entirely thwart the forces of nature, but one may make some progress with the help of engineering.
When natural disasters like earthquakes, floods, etc. occur, infrastructures are most likely to suffer the greatest losses.
It is important to plan properly for future mishaps while taking current ones into consideration during the construction of a building in order to avoid these disasters.
It is important to understand what earthquakes are and how they are caused before trying to build earthquake-resistant buildings.
Earthquake
Earthquakes are defined as sudden shaking or disruptions of a layer of the earth that cause shock waves to travel through the lithosphere and cause seismic activity to occur beneath it.
The seismic energy waves travel through the earth and cause the shaking that is commonly referred to as an earthquake.
An explanation for why buildings fail during earthquakes
Instability of the foundation
Although any structure can carry its own weight, it is not designed particularly to resist irregular, multidirectional, and intense side-to-side loads that occur during an earthquake that can cause the structure to collapse due to the irregular, multidirectional, and intense side-to-side loads that occur during an earthquake.
Material Failure
The failure of a building during an earthquake is often caused by poor-quality materials or building materials that are not able to withstand seismic vibrations.
The Failure Of Design
In the event of an earthquake, a structure that does not possess the ability to withstand seismic waves, and is not designed to withstand high ductility, may result in an earthquake-induced disaster.
Failure of the soil
There is a possibility that an earthquake can create a force that is powerful enough to transform soft soil into quicksand, thus making it incapable of supporting the weight of the structure
The failure of joints
As a consequence, when the clearance between structures is inadequate, and when joints between columns and beams are too rigid to bend, the structure could collapse during an earthquake if there is not sufficient clearance.
How can you make an Earthquake Resistant Building?
It is easier for the infrastructure to crumble during natural calamities like earthquakes, Tsunamis, etc. However, if you want to make sure your building is built earthquake-resistant, you should take the following considerations into consideration.
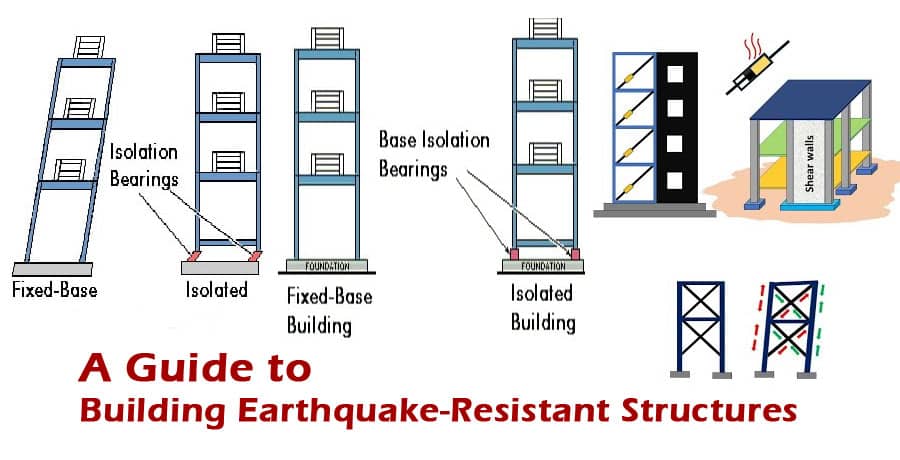
Foundations that are resistant
Any construction must have a solid foundation that carries the structure's load in order for the structure to be built. However, a foundation of the same type cannot be applied to all structures. Each foundation must be designed based on its needs.
If you want to build an earthquake-resistant building, you must place it on top of pads that are usually made from steel, rubber, and lead.
It prevents seismic waves from passing through the building and separates it from the ground. The building stays steady when an earthquake occurs because only the pads move.
Devices for controlling vibrations
A variety of structural designs have demonstrated that vibration control devices are most effective in mitigating seismic hazards. Energy absorption is commonly achieved with these vibrational control devices.
A high-rise building with a mid- or high-rise roof is usually equipped with these devices as they will serve as an energy-absorbing system that can withstand the effects of earthquakes and wind.
System For Cross Bracing
In a building structure, the use of a cross bracing system can be an effective way to build earthquake-resisting buildings that are constructed in areas where diagonal supports intersect. This is especially true in buildings constructed in areas that are vulnerable to earthquakes. The layout of a cross brace on a bridge can be determined by the placement of the two diagonal supports in an X-shaped pattern in the form of a cross.
A lateral force such as wind waves or seismic waves will exert pressure on this bracing during an earthquake. The tension in one brace will cause the compression in the other.
Diaphragm
Diaphragms are basically floors and roofs that are used to transfer the lateral forces of a building to the vertical components within it.
As required during earthquake shaking, the diaphragm also maintains and transmits force between vertical elements
Building structures should take into account the seismic force-resisting system of diaphragms when designing earthquake-resistant buildings.
Material that is earthquake-resistant should be used
In order to construct earthquake-resistant buildings, it is important to consider the quality of the building materials, as the lower the quality, the more vulnerable it will be to earthquakes.
It is imperative that the materials used in the fabrication of the parts must be highly ductile and capable of undergoing large deformations and tensions. There are some materials, such as steel, and wood, that are highly ductile and can withstand earthquakes. Hence, it is recommended that only the most tested and proven materials should be used for building structures.
A few years ago, industrial innovations led to the development of a number of new building materials which were designed to retain their shape for a longer period of time than standard materials, such as Memory alloy - this material can withstand heavy strains and can return to its original shape afterwards.
Consideration of load
Structures are always designed according to their load considerations, with a stronger foundation for a larger load. It is possible to add additional weight to the structure of a building by adding additional structures.
Generally, tall structures are usually in a narrow shape as they move up the building structure because their surfaces on the lower floors are wider than their surfaces on the upper floors, so if a building is damaged by an earthquake, the lower floors are less likely to crumble.
Concrete and bonding stirrups weaken during the earthquake, causing the structure to collapse. In order to strengthen the structure of the building, one can take into consideration Polyurethane (PU), which is a lightweight insulated panel with the highest insulating factor.
Please watch the following Short video for Building Earthquake-Resistant Structures
