What causes soil subsidence & prevented?
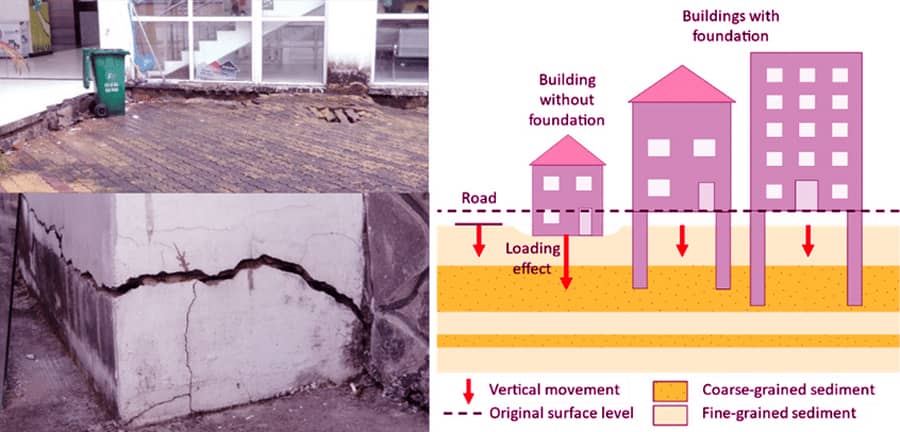
Due to the withdrawal of moisture, the ground beneath a building slides downward. As a result, the foundation sinks, compromising the structure's stability.
Shrinkage of soil occurs when moisture is extracted, causing the foundation to move downward. As a result of soil desiccation caused by trees or other vegetation, clay soil usually subsides.
Define Subsidence
A structure's subsidence can be diagnosed early by recognizing the signs and considering appropriate measures. Cracks in slabs without intersections, outward movement of exterior walls at the top, and cracks in slabs that grow in dry months but close in wet months are symptoms of subsidence.
Signs of Soil Subsidence
- The superstructure typically experiences wider cracks in the dry season and smaller cracks in the wet season.
- Brick walls have cracks that run diagonally across their interiors and exteriors.
- Compared to their width at the bottom, they are wider at the top.
- Cracks are larger than 3 mm in width.
- It is visible near the windows and doors that there are cracks.
- Recent changes in the soil moisture beneath the foundation have resulted in a decrease in moisture content.
- Concrete slabs have single lines of cracks, which have no intersections.
- The topmost walls of a building move outward.
- There is a problem with the concrete driveway.
- Level distortions of the foundation increase with time and seasonally, especially in dry months, according to time change elevations.
- The bowl shaped foundation has a low point near its center, which rose around its perimeter several years ago.
- The exterior foundation grade beam does not have a gap between it & the adjacent soil at grade, especially during the dry season.
- More than 25 is the plasticity index of soil.
- When excavating, the soil beneath the grade beam is dry, more than 2.5 cm to 5 cm deep.
- The roots of a large tree extend toward the structure at grade.
Causes of Soil Subsidence
Soil subsidence can be caused by many factors, including tree roots from willow, ash, and oak trees. It is possible for a tree to absorb moisture and water from the soil beneath your home if it grows too close to your property. Consequently, this dries out the soil and causes it to become unstable.
Subsidence can also be caused by the soil on which the property was built. The spongy properties of clay cause the soil to shrink when dried and pull away from foundations, thus weakening their support. If there is any water leak underneath a property with a high gravel or sand content, the soil can be washed away.
At first, leaking water may not seem like a serious problem. Broken drainage can cause water to leak into the soil and under your property, washing away the soil beneath your foundations. The foundation can also give way and subside if there is flooding near your home.
Solution of Soil Subsidence
You should seek professional help as soon as you discover the problem. A structural engineer can determine the soil subsidence cause and determine the best course of action. You can also get advice from a structural engineer on how to resolve the issue.
It removes a tree whose roots have caused soil subsidence to avoid further damage. It may be necessary to unpin a property in the worst cases of subsidence.
That will require concrete or pile addition to your foundations. Structural engineers will be able to provide ideas on how to strengthen your property as well as reduce the impact of further subsidence.
Wrapping it Up
An unstable property could face major problems due to soil subsidence. Ground movement or weakening under a property can cause some foundations to be displaced. A move or sinking on one side of the property may affect the whole structure of the property. In addition to cracks appearing, this can also cause structural damage.
