Bar Bending Schedule (BBS) for Pile Foundation: A Comprehensive Guide
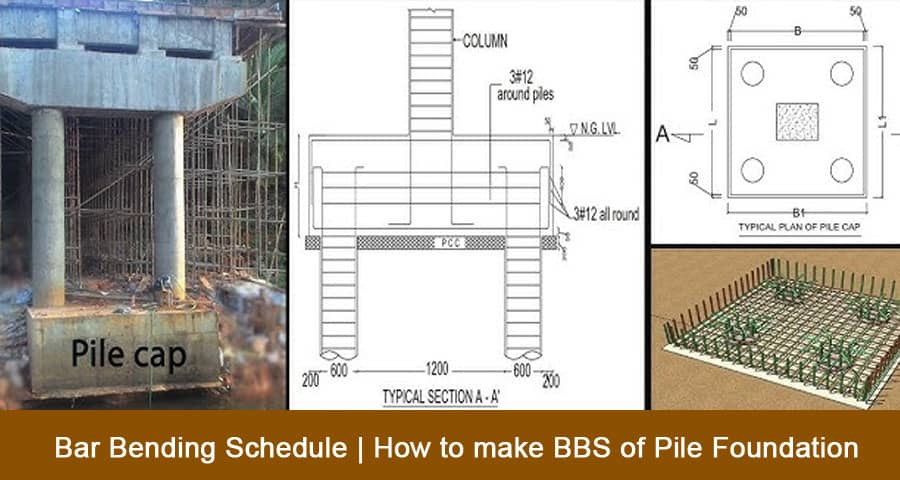
Bar Bending Schedule (BBS) is a critical component in the construction process, especially for pile foundations. Properly understanding and preparing a BBS ensures the correct quantity of reinforcement bars (rebars) are used, reducing waste and optimizing structural integrity.
What is a Bar Bending Schedule (BBS)?
A Bar Bending Schedule (BBS) is a chart that lists the type, size, length, and number of reinforcement bars required for a specific structural element. In the context of pile foundations, BBS helps in detailing how the steel reinforcement should be cut, bent, and placed. This ensures that the structural load is properly transferred from the structure to the foundation.
Importance of BBS in Pile Foundation
For pile foundations, BBS plays a crucial role in:
- Ensuring Accuracy: A well-prepared BBS eliminates errors in cutting and bending, leading to precise reinforcement.
- Cost Efficiency: By accurately estimating the amount of steel required, wastage is minimized, which in turn reduces costs.
- Structural Integrity: Properly detailed bars ensure that the pile foundation can bear the intended load, providing safety and stability to the structure.
Components of a Pile Foundation BBS
When preparing a BBS for pile foundations, several components must be considered:
- Type of Piles: Bored piles, driven piles, or screw piles, each type has specific reinforcement requirements.
- Rebar Details: Information about the diameter, length, and shape of the rebars.
- Covering Requirements: The necessary concrete cover that protects the steel from corrosion.
- Lap Length and Anchorage: The overlap of bars to ensure proper load transfer.
Step-by-Step Guide to Preparing BBS for Pile Foundation
1. Understand the Structural Drawings
The first step in preparing a BBS is to thoroughly review the structural drawings provided by the engineer. These drawings include details on the dimensions, load-bearing requirements, and the type of reinforcement required.
2. Calculate the Length of Rebars
For each section of the pile, calculate the required length of the rebars. This includes:
- Vertical Bars: Calculate the full depth of the pile, ensuring adequate overlap where necessary.
- Spiral or Circular Ties: For circular piles, calculate the length based on the diameter and spacing specified in the design.
- Stirrups: These are usually used in the top sections of piles to provide additional shear strength.
3. Determine the Number of Rebars
Next, determine the number of rebars required for each section of the pile. This is based on the spacing provided in the design drawings. For instance:
- Vertical Reinforcement: Often spaced equally around the circumference of the pile.
- Ties or Hoops: Typically spaced closer at the top and bottom of the pile where bending moments are higher.
4. Bar Cutting and Bending
Once the lengths and quantities are determined, the next step is to cut and bend the bars according to the specifications. This should be done precisely as per the BBS to avoid any errors that could lead to structural issues.
5. Prepare the BBS Chart
The final step is to compile all the data into a BBS chart. This chart should include:
- Bar Mark: A unique identifier for each type of rebar.
- Bar Shape: The shape code as per the standard codes (e.g., straight, L-bend, U-bend).
- Diameter: The diameter of the rebar in millimeters.
- Length: The total length of the rebar.
- Quantity: The number of bars required for the section.
- Weight: The weight of the steel bars, which can be calculated using the formula:
Weight = Length x Unit Weight
6. Check for Compliance with Standards
Ensure that the BBS complies with the relevant building codes and standards, such as IS 2502 for bending and IS 456 for concrete structures in India. Compliance guarantees that the pile foundation will meet all safety and durability requirements.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Pile Foundation BBS
- Incorrect Bar Length Calculation: This can lead to inadequate lap lengths, compromising the structure's integrity.
- Overlapping Errors: Ensure that overlaps are placed where moments are minimal to avoid stress concentrations.
- Ignoring Cover Requirements: Insufficient cover can lead to corrosion of the steel, significantly reducing the lifespan of the pile foundation.
- Misplacement of Bars: Bars should be placed precisely as per the BBS to ensure the load is properly distributed.
Advantages of a Well-Prepared BBS
A well-prepared BBS for pile foundations offers several advantages:
- Improved Construction Efficiency: Workers can cut and bend bars accurately and quickly, reducing labor time.
- Material Optimization: Minimizes steel wastage by ensuring that only the required amount is used.
- Enhanced Structural Safety: Correctly reinforced piles ensure that the foundation can handle the loads imposed by the structure.
- Cost Savings: By reducing wastage and optimizing labor, overall construction costs are significantly reduced.
Conclusion
In the construction of pile foundations, a Bar Bending Schedule (BBS) is not just a technical document but a critical tool that ensures the durability, safety, and efficiency of the foundation. Proper preparation of a BBS requires meticulous attention to detail, thorough understanding of structural drawings, and adherence to relevant standards. By following the guidelines outlined in this article, engineers and contractors can ensure that their pile foundations are constructed to the highest standards, offering long-term performance and safety.
