How to Calculate the Quantity of Bricks in One Cubic Meter
Calculating the quantity of bricks required per cubic meter is essential for construction planning. It allows for precise budgeting, ordering, and material usage.
What is a Cubic Meter in Brickwork?
A cubic meter is a standard unit of volume used in construction to measure the space bricks will occupy. Knowing how many bricks fit into one cubic meter helps estimate the exact amount needed for a specific area, reducing waste and keeping project costs in check.
Standard Brick Size and Mortar Joint Considerations
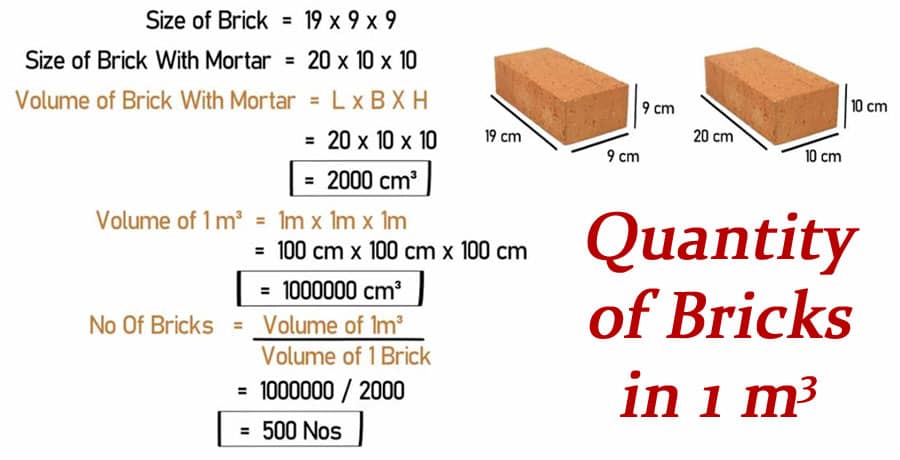
Brick size can vary, so understanding the dimensions of the bricks used is crucial. The most commonly used brick size worldwide is 190 mm x 90 mm x 90 mm. However, this can vary depending on local standards and brick types.
Mortar Thickness
Mortar, the bonding material between bricks, affects the final calculations. For standard calculations, a 10 mm (1 cm) mortar joint thickness is commonly assumed. This thickness impacts the number of bricks per cubic meter, as it adds volume around each brick.
How to Calculate the Quantity of Bricks Per Cubic Meter
To calculate how many bricks are required per cubic meter, follow these steps:
1. Determine the Volume of a Single Brick (with Mortar)
To calculate the total number of bricks per cubic meter, start by determining the volume of a single brick, including the mortar.
For example, for a standard brick size of 190 mm x 90 mm x 90 mm, adding the mortar thickness (10 mm) to each dimension results in:
- Length with mortar = 190 mm + 10 mm = 200 mm
- Width with mortar = 90 mm + 10 mm = 100 mm
- Height with mortar = 90 mm + 10 mm = 100 mm
Now, convert these dimensions from millimeters to meters:
- Length = 0.2 m
- Width = 0.1 m
- Height = 0.1 m
The volume of one brick (with mortar) is:
0.2m x 0.1m x 0.1m = 0.002 cubic meters
2. Calculate Total Bricks Needed for One Cubic Meter
To find the quantity of bricks in one cubic meter, divide 1 cubic meter by the volume of one brick (with mortar):
Number of bricks per cubic meter = 1 cubic meter / 0.002 cubic meters per brick = 500 bricks
Key Considerations in Brick Quantity Calculations
Several variables can affect brick quantity calculations:
- Brick Size Variations: Standard brick sizes can vary by region, altering the total count.
- Mortar Joints: Adjusting the thickness of the mortar joint will impact the total brick quantity.
- Allowances for Breakage and Waste: Add an extra 5-10% to account for brick breakage or cutting during construction.
Example Calculations for Different Brick Sizes
Example 1: Modular Brick (230 mm x 110 mm x 75 mm)
Assuming a 10 mm mortar joint:
- Length = 230 mm + 10 mm = 240 mm = 0.24 m
- Width = 110 mm + 10 mm = 120 mm = 0.12 m
- Height = 75 mm + 10 mm = 85 mm = 0.085 m
The volume of one brick (with mortar) is:
0.24 x 0.12 x 0.085 = 0.002448 cubic meters
Then, calculate the number of bricks per cubic meter:
1 cubic meter / 0.002448 cubic meters per brick ≈ 408 bricks
Example 2: Metric Brick (215 mm x 102.5 mm x 65 mm)
Assuming a 10 mm mortar joint:
- Length = 215 mm + 10 mm = 225 mm = 0.225 m
- Width = 102.5 mm + 10 mm = 112.5 mm = 0.1125 m
- Height = 65 mm + 10 mm = 75 mm = 0.075 m
Volume of one brick (with mortar):
0.225 x 0.1125 x 0.075 = 0.0018984 cubic meters
Total bricks per cubic meter:
1 cubic meter / 0.0018984 cubic meters per brick ≈ 527 bricks
Adjustments for Efficiency in Construction Planning
When estimating bricks for a project, it's essential to consider specific construction factors and planning strategies.
Accounting for Wastage
Adding a 5-10% buffer for wastage covers unexpected needs, such as chipped or broken bricks, particularly in large projects.
Considerations for Complex Patterns and Designs
Projects that include intricate brick patterns or special design features require additional calculations to determine brick quantities accurately.
Practical Tips for Brick Quantity Calculation
- On-Site Measurement Verification: Verify dimensions and mortar thickness on-site to refine calculations and reduce margin for error.
- Using Software for Estimation: Consider using construction estimation software to simplify calculations.
- Factor in Regional Standards: Consult local construction standards or guidelines to ensure compatibility with common brick sizes and practices.
Calculating the number of bricks per cubic meter is a foundational skill in construction planning. A precise approach to this calculation not only aids in cost estimation but also minimizes waste and supports efficient resource management.
Advantages of Proper Brick Calculation
Understanding brick quantity calculations has multiple advantages beyond just accurate budgeting and ordering. Here are a few reasons precise calculations are essential for efficient and sustainable construction:
- Reduced Material Wastage: Precise brick quantities lead to fewer leftover bricks, reducing waste and helping the environment.
- Improved Cost Management: Proper calculations prevent overspending on materials and labor by ensuring only the required bricks are purchased.
- Enhanced Structural Integrity: Accurate estimations help achieve the intended structural strength and longevity without over-relying on fillers or ad-hoc adjustments.
Conclusion
Calculating the number of bricks in one cubic meter is a fundamental step in construction that influences budgeting, planning, and material usage. By understanding brick size, mortar thickness, and other factors such as bond patterns and regional conditions, builders can achieve accurate estimates that support efficient, sustainable, and cost-effective construction.
For more information, please watch the video tutorial
