How to Calculate Quantity of Steel in RCC Slab, Column & Beam
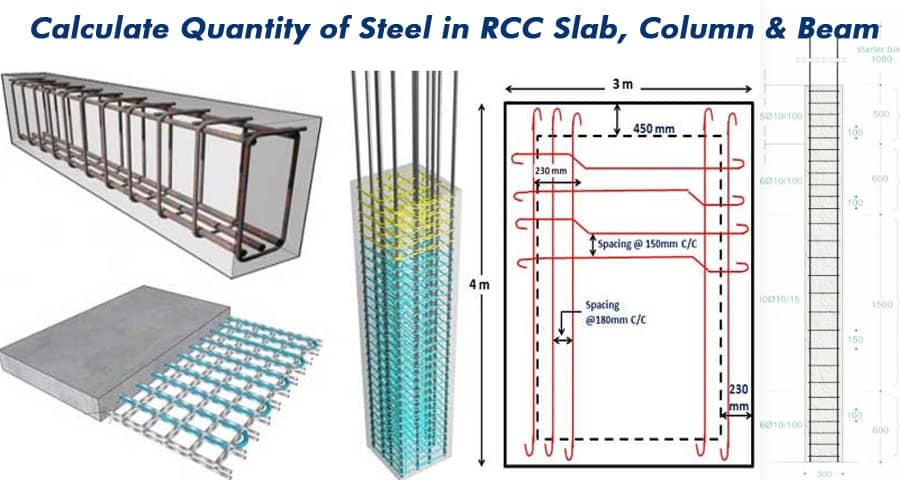
Calculating the quantity of steel required in Reinforced Concrete Cement (RCC) structures is a crucial step in construction planning and execution. It ensures structural integrity, durability, and adherence to safety standards.
Understanding the Basics
Before delving into calculations, it's imperative to grasp the fundamental concepts of RCC construction. RCC comprises concrete and steel reinforcement bars (rebars) arranged in a manner that harnesses the strengths of both materials. Concrete provides compressive strength, while steel rebars offer tensile strength, making the structure robust and resilient.
Factors Affecting Steel Quantity Calculation
Several factors influence the quantity of steel required in RCC structures:
- Structural Design: The structural design, including the load-bearing capacity, span, and intended use of the structure, directly impacts the steel quantity. Heavier loads and longer spans necessitate additional reinforcement.
- Building Codes and Standards: Adherence to local building codes and standards is imperative for ensuring structural safety and compliance. These regulations specify minimum reinforcement requirements based on factors such as seismic activity, soil conditions, and building height.
- Concrete Mix Design: The type and grade of concrete used in construction play a crucial role in determining the steel quantity. Higher strength concrete may require lesser reinforcement compared to lower strength mixes.
Calculating Steel Quantity in RCC Slabs
RCC slabs are horizontal structural members that support loads from above. Calculating the steel quantity in slabs involves the following steps:
- Determine Bar Bending Schedule (BBS): Prepare a detailed bar bending schedule specifying the diameter, spacing, and length of reinforcement bars required for the slab.
- Calculate Total Length of Bars: Multiply the length and width of the slab to obtain the total area. Then, multiply this by the desired spacing between bars to determine the total length of bars required.
- Account for Overlaps and Wastage: Factor in overlaps at bar junctions and wastage during cutting and bending of bars.
- Consider Distribution Bars: Include additional bars, known as distribution bars, along the shorter span of the slab to distribute loads evenly.
Estimating Steel Quantity in RCC Columns
RCC columns are vertical structural members designed to support loads from above. Estimating the steel quantity in columns involves similar steps:
- Calculate Cross-sectional Area: Determine the cross-sectional area of the column using its dimensions.
- Derive Reinforcement Ratio: Based on structural design requirements, calculate the reinforcement ratio (percentage of steel area to column area).
- Compute Steel Quantity: Multiply the cross-sectional area by the reinforcement ratio to obtain the quantity of steel required in the column.
Determining Steel Quantity in RCC Beams
RCC beams are horizontal members that transfer loads to columns or walls. Calculating the steel quantity in beams follows these steps:
- Determine Moment of Inertia: Calculate the moment of inertia of the beam section to assess its bending capacity.
- Establish Bending Moment: Analyze the applied loads and support conditions to determine the bending moment acting on the beam.
- Calculate Steel Area: Utilizing the bending moment and allowable stress of steel, compute the required steel area using beam design formulas.
For more information, please watch the following video tutorial
Source: Civil Tutor
Conclusion
Accurate calculation of the quantity of steel in RCC structures is paramount for ensuring structural stability, durability, and safety. By understanding the underlying principles and following meticulous calculation methods, engineers and construction professionals can optimize material usage and enhance project efficiency.
