Calculation Formula of Column, Beam and Slab
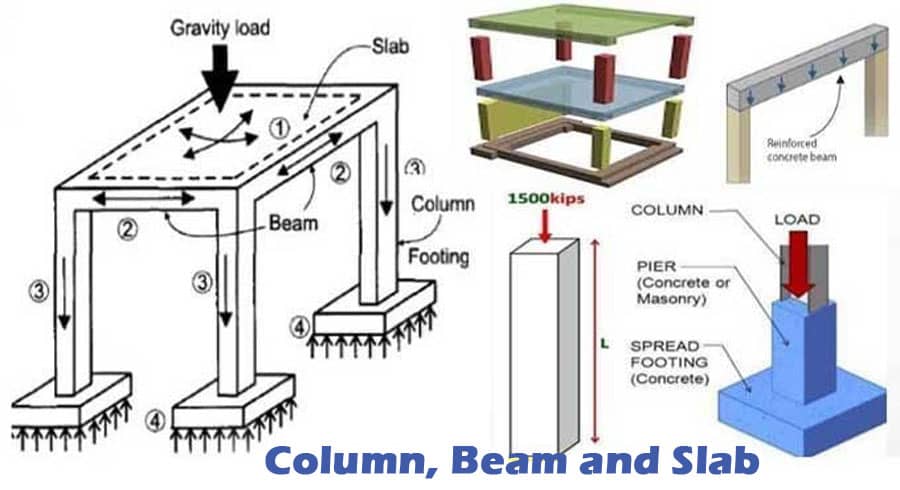
In the construction industry, the calculation formula of columns, beams, and slabs is essential for ensuring the safety and stability of a building. These three elements play a vital role in the overall structure of a building, and accurate calculations are necessary to ensure their strength and durability.
Introduction
Building construction involves various elements, including columns, beams, and slabs, that provide support and stability to the overall structure. The calculation formula of these elements is crucial in ensuring their strength and durability, preventing any risk of collapse or structural failure. The calculation process involves various parameters and factors, including material strength, load-bearing capacity, and structural design. In this article, we will explore the calculation formula of columns, beams, and slabs.
Column Calculation Formula
A column is a vertical element that provides support to the building structure. The calculation formula for columns involves the following parameters:
Cross-sectional area
The cross-sectional area of the column is calculated by multiplying the width and height of the column.
Moment of inertia
The moment of inertia is a measure of a column's resistance to bending. It is calculated by using the column's cross-sectional area and distance from the centroidal axis.
Load-bearing capacity
The load-bearing capacity of a column is calculated based on the material strength, cross-sectional area, and height of the column. The load-bearing capacity should be higher than the maximum load expected to be placed on the column.
Formula
The calculation formula for columns is as follows:
Load-bearing capacity = Material strength x Cross-sectional area x Height
Beam Calculation Formula
A beam is a horizontal element that provides support to the building structure. The calculation formula for beams involves the following parameters:
Moment of inertia
The moment of inertia is a measure of a beam's resistance to bending. It is calculated by using the beam's cross-sectional area and distance from the centroidal axis.
Cross-sectional area
The cross-sectional area of the beam is calculated by multiplying the width and height of the beam.
Load-bearing capacity
The load-bearing capacity of a beam is calculated based on the material strength, cross-sectional area, and length of the beam. The load-bearing capacity should be higher than the maximum load expected to be placed on the beam.
Formula
The calculation formula for beams is as follows:
Load-bearing capacity = Material strength x Cross-sectional area x Length
Slab Calculation Formula
A slab is a horizontal element that forms the floors or ceilings of a building. The calculation formula for slabs involves the following parameters:

Thickness
The thickness of the slab is calculated based on the maximum load expected to be placed on the slab.
Reinforcement
Reinforcement is required to increase the tensile strength of the slab. The amount of reinforcement required is calculated based on the maximum load expected to be placed on the slab.
Load-bearing capacity
The load-bearing capacity of a slab is calculated based on the material strength, thickness, and reinforcement of the slab. The load-bearing capacity should be higher than the maximum load expected to be placed on the slab.
Formula
The calculation formula for slabs is as follows:
Load-bearing capacity = Material strength x Thickness x Reinforcement
Conclusion
The calculation formula of columns, beams, and slabs is essential in ensuring the safety and stability of a building. The calculation process involves various parameters and factors, including material strength, load-bearing capacity, and structural design. Accurate calculations of these elements are necessary to ensure their strength and durability, preventing any risk of collapse or structural failure.
Please watch the following short Video
