Movable Bridges & Its Types
Movable bridges, an ingenious feat of engineering, have played a pivotal role in facilitating both land and maritime transport in regions where traditional fixed bridges would impede navigational channels. These bridges are designed to allow passage for vessels of various sizes without permanently obstructing the roadway or rail tracks that cross them.
What Are Movable Bridges?
Movable bridges are mechanically operated structures designed to change position to allow for the passage of boats and ships. Unlike fixed bridges, they offer greater flexibility in areas with heavy marine traffic. These bridges are typically found over navigable waterways and are an essential element in urban infrastructure where space and utility must be maximized.
Advantages of Movable Bridges
- Efficient use of space in congested urban or riverine environments
- Reduced construction costs compared to high fixed bridges
- Enhanced navigability for maritime vessels
- Versatility in infrastructure development
- Preservation of historical and cultural waterfronts
Main Types of Movable Bridges
Understanding the different types of movable bridges is essential for urban planners, civil engineers, and infrastructure investors. Each type has its distinct advantages and operational methods.
1. Bascule Bridges

One of the most popular and efficient types, bascule bridges function much like a seesaw. The bridge deck is split into two leaves or a single leaf that pivots upward using a counterweight system. These bridges open quickly and require minimal horizontal space, making them ideal for busy water routes.
Famous Example:
Tower Bridge in London is perhaps the most iconic double-leaf bascule bridge, combining aesthetic elegance with functionality.
Advantages:
- Fast operation
- Energy efficiency due to counterweights
- Suitable for high-traffic areas
2. Swing Bridges
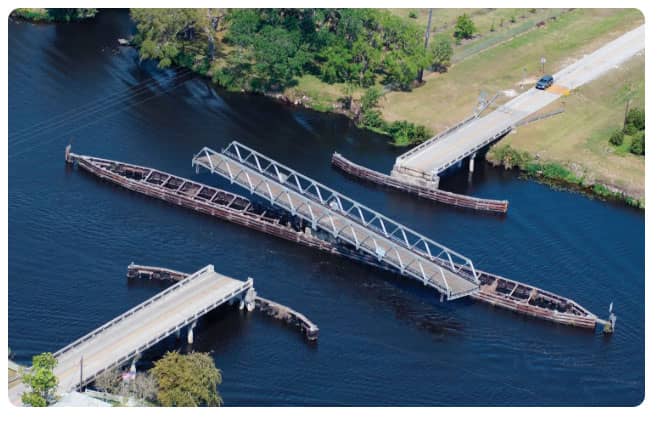

Swing bridges operate by rotating horizontally around a central pivot point, allowing vessels to pass on either side of the rotating span. These bridges are particularly useful over wide rivers or canals where vertical clearance isn't feasible or necessary.
Famous Example:
Pont Jacques-Cartier Swing Bridge in Canada is a key structure demonstrating the adaptability of this design.
Advantages:
- Can accommodate multiple waterway channels
- Low maintenance compared to lift mechanisms
- Cost-effective for large spans
3. Vertical Lift Bridges
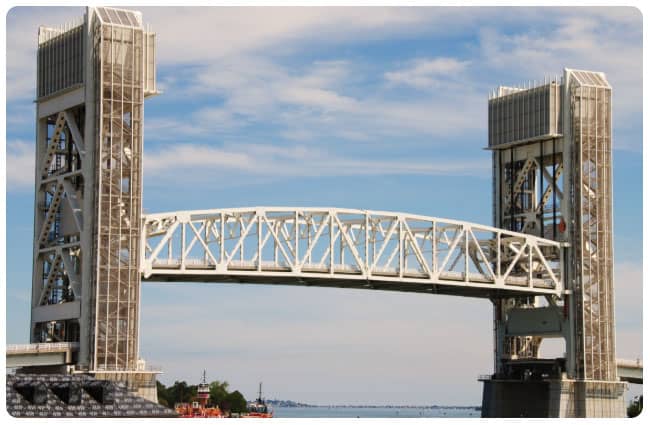

A vertical lift bridge raises its span vertically while remaining horizontal. Towers on either side of the bridge house pulleys and counterweights to raise and lower the deck. These bridges are ideal for railroads and highways that require consistent and stable alignment.
Famous Example:
Arthur Kill Vertical Lift Bridge, connecting Staten Island and New Jersey, is the longest vertical lift bridge in the United States.
Advantages:
- Higher vertical clearance than swing or bascule bridges
- Stable deck alignment
- Suitable for heavy rail traffic
4. Retractable Bridges
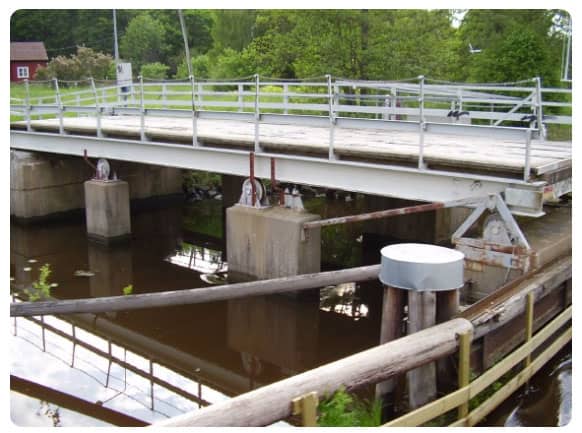

Also known as sliding bridges, retractable bridges work by sliding the deck back horizontally to clear the waterway. This type is less common due to the requirement for extensive lateral space, but it is particularly effective in tight, controlled environments such as canals or docks.
Famous Example:
The Gateshead Millennium Bridge in England features a unique tilting design, often categorized under retractable movement types.
Advantages:
- Sleek and modern design
- Less visual obstruction when open
- Lower mechanical complexity
5. Folding Bridges
These bridges incorporate multiple hinged segments that fold up like an accordion. They are rare and typically used in pedestrian or light vehicle traffic zones.
Famous Example:
The Hörn Bridge in Kiel, Germany is a striking example of a three-segment folding bridge used primarily for pedestrian traffic.
Advantages:
- Visually impressive
- Minimal impact on surrounding architecture
- Ideal for narrow waterways
6. Submersible Bridges
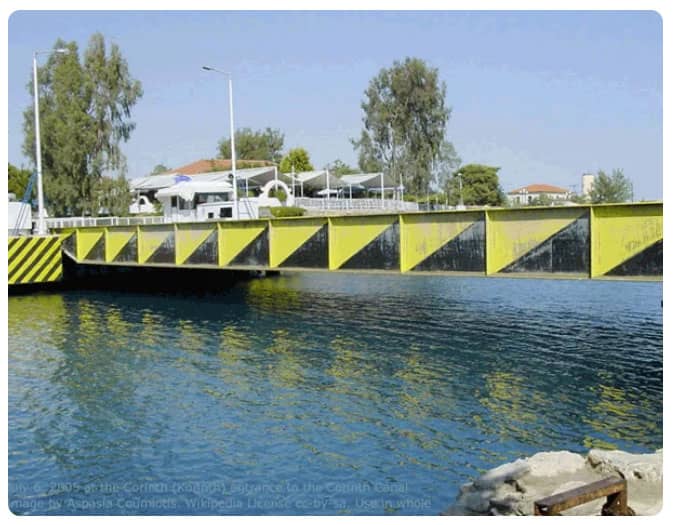

Submersible bridges lower their deck beneath the water to allow marine traffic to pass over. While highly specialized, these bridges are used in locations where vertical and horizontal movement is restricted.
Advantages:
- No overhead obstructions
- Minimal visual disruption
- Useful in military and industrial applications
Applications of Movable Bridges
Movable bridges serve both functional and aesthetic purposes, making them ideal for:
- Urban waterfront developments
- Commercial shipping lanes
- Rail and vehicle transit hubs
- Tourist attractions and iconic landmarks
- Military and industrial installations
Challenges in Movable Bridge Design
While movable bridges offer substantial benefits, they also pose unique engineering challenges:
- High initial construction costs
- Complex mechanical systems requiring regular maintenance
- Operational downtime due to weather or mechanical failure
- Traffic delays during opening/closing cycles
Technological Innovations in Movable Bridges
Modern movable bridges are incorporating cutting-edge technologies, including:
- Hydraulic actuation systems for faster, quieter movement
- Remote monitoring and automated control systems
- Sustainable energy solutions, such as solar or regenerative braking
- Advanced materials, such as carbon fiber composites for reduced weight
Movable Bridges in Urban Planning
Cities with significant waterways rely on strategically placed movable bridges to enhance connectivity without compromising shipping activity. Urban planners are increasingly incorporating such bridges into multi-modal transport ecosystems, ensuring that pedestrians, cyclists, vehicles, and ships can all coexist seamlessly.
Conclusion
Movable bridges are more than just architectural feats - they are functional masterpieces that balance the needs of land and maritime traffic with elegance and efficiency. From bascule to vertical lift, each type of movable bridge offers unique advantages tailored to its environment and purpose. As technology advances, we expect these structures to become even more intelligent, durable, and sustainable, reinforcing their place in the future of global infrastructure.
Please view the following short video for Movable Bridges & Its Types
