The Guide to Road Patterns: Types and Advantages

Welcome to our comprehensive guide on road patterns. Whether you're a civil engineer, urban planner, or simply interested in understanding the infrastructure around you, this guide will provide valuable insights into the world of road design.
Understanding Road Patterns
Road patterns refer to the layout or arrangement of streets, lanes, and thoroughfares within a city or town. These patterns play a crucial role in shaping the flow of traffic, pedestrian movement, and overall accessibility. By carefully designing road patterns, urban planners aim to create efficient, safe, and aesthetically pleasing environments for residents and visitors alike.
Types of Road Patterns
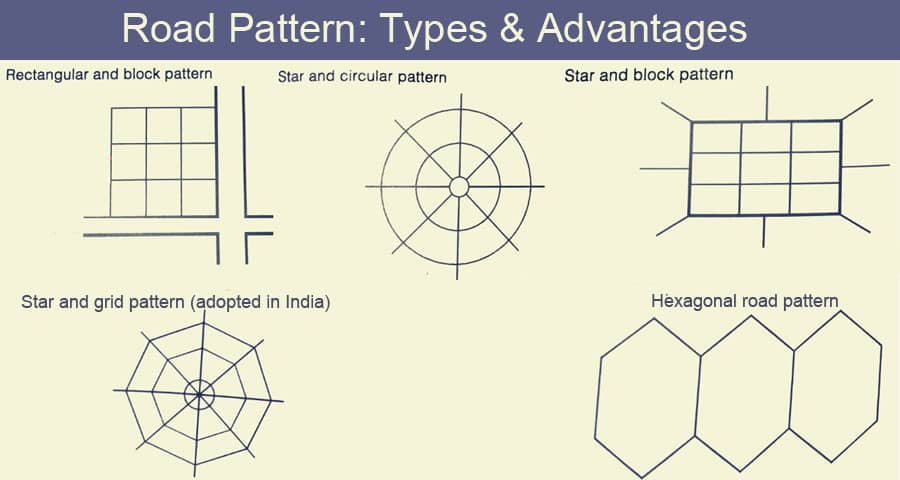
- Grid Pattern: One of the most common road patterns, the grid layout features streets that intersect at right angles, forming a series of squares or rectangles. This pattern promotes ease of navigation and efficient land use, making it popular in many urban areas.
- Radial Pattern: In a radial road pattern, streets radiate outward from a central point, often a city center or focal landmark. This design is particularly common in cities with a centralized core, such as those built around historical landmarks or natural features.
- Circular Pattern: Circular road patterns consist of concentric rings or loops that encircle a central area. This layout is often found in cities with circular topography or those designed around a central plaza or park.
- Irregular Pattern: As the name suggests, irregular road patterns do not adhere to any specific geometric arrangement. Instead, streets may meander, curve, or intersect at various angles, reflecting the organic growth and development of older cities or neighborhoods.
- Herringbone Pattern: This unique road pattern features streets that intersect at acute angles, resembling the bones of a fish. While less common than other layouts, the herringbone pattern can offer visual interest and improve traffic flow in certain contexts.
Advantages of Road Patterns
- Efficient Traffic Flow: Well-designed road patterns can minimize congestion, reduce travel times, and improve overall traffic flow. By optimizing the layout of streets and intersections, planners can enhance the movement of vehicles through a city or town.
- Enhanced Safety: Certain road patterns, such as grids and radial designs, offer improved safety for motorists, cyclists, and pedestrians. Clear, logical layouts with designated lanes and crossings help reduce the risk of accidents and collisions.
- Better Accessibility: A well-planned road network increases accessibility for residents, businesses, and visitors alike. By providing multiple routes and modes of transportation, cities can ensure that people can easily reach their destinations, whether by car, public transit, or on foot.
- Urban Revitalization: Strategic road patterns can contribute to the revitalization of urban areas, encouraging economic development, investment, and community engagement. By creating inviting streetscapes and pedestrian-friendly environments, cities can attract new residents and businesses.
- Aesthetic Appeal: Finally, road patterns play a significant role in shaping the visual identity and character of a city or neighborhood. Thoughtfully designed streetscapes, landscaping, and architectural elements can enhance the overall aesthetic appeal and livability of an area.
Conclusion
In conclusion, road patterns are a fundamental aspect of urban design and planning, influencing everything from traffic flow to community identity. By understanding the various types of road patterns and their associated advantages, planners and policymakers can make informed decisions to create vibrant, sustainable, and inclusive cities for the future.
please watch the following short video for Road Patterns
